Depletion of Vegetal Resources in Niger Delta: A Challenge to Environmental Sustainable Development
Article Information
Aloni Clinton1, Alexander Chinago B2*
1Department of Transportation Planning and Logistics, Captain ElechiAmadi Polytechnic, Rumuola, Port Harcourt
2Department of Transportation Planning and Logistics, School of Environmental Sciences, Captain ElechiAmadi Polytechnic, Rumuola, Port Harcourt, Rivers State
*Corresponding author: Dr.Alexander Chinago B, Department of Transportation Planning and Logistics, School of Environmental Sciences, Captain ElechiAmadi Polytechnic, Rumuola, Port Harcourt, Rivers State
Received: 10th Jan-2019; Revised: 25th Feb-2019; Accepted: 28th Feb-2019;
Copyright: ©2019 Dr.Alexander Chinago B. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited
Citation: Aloni Clinton , Alexander Chinago B. Depletion of Vegetal Resources in Niger Delta: A Challenge to Environmental Sustainable Development. International Journal of Plant, Animal and Environmental Sciences 9 (2019): 26-32.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Vegetal resources abound in the Niger Delta region, and it serves great purpose, but unplanned
development and weak policy on environmental sustainability is a threat to man, biodiversity and the environment. The importance of vegetal resources can never be over emphasized, it absorb carbon dioxide, protect the wildlife, the soil, enhance quality of air, provide fuel for homes, medicine for the sick, fund for government and individual etc. With depleted vegetal resources, the rate of flooding, soil erosion, and pollution has increased. The atmospheric temperature is slowly but steadily increasing, wind becoming more destructive; further the extinction of some plants and animals among others are few consequences of vegetal depletion. The stand of this paper is that sustainable development, such that will judiciously use and enjoy the vegetal resources without short changing future generation should be pursued. Base on this, the following suggestions were made- afforestation and reforestation be urgently practise. The brown areas of urban centres should be built upon and the green areas conserved. Strong legislation against the depletion of vegetal resources is needed. Forest reserves should be created to protect endangered species. Life will be meaningful when the vegetation coexists with man. We did not inherit the vegetation from our fathers, as to treat it any how we like. It is a legacy that we must protect or be doomed.
Keywords
Depletion; Endangered species, Niger Delta, Sustainable Development, Vegetal resources
Article Details
INTRODUCTION
Development is an effort towards better physically as well determination of a community to strive malalui series of combination of processes of social, economic and institutional order to achieve a better life [1]. The term development has been defined as a comprehensive economic, social, cultural and political process which aims at the constant improvement of the well-being of the entire population and of the individuals on the basis of their active, free and meaningful participation in development process and in the fair distribution of benefits resulting there-from [2].In developing countries of the world emphasis are given to physical and economic development than sustainable development. Reason being that the huge gap between developed and developing nations need to be abridged. In the quest to attain physical and economic development to minimize the gap between developed and developing countries, environmental resources were unduly over stretched, living a negative mark or foot print on the environment.
The development experienced in most developing countries especially in tropical Africa were more of accidental than planned development [3].
Development was based on extraction of raw materials and other available resources to service planned development in Western Europe and North America; and indiscriminate deforestation to build houses, roads, airports, stadiums and schools, etc. just to have similar things in developed countries at home.The side effect of unplanned development can be seen everywhere in developing nations and especially in fragile Niger Delta environment. d’Huart [4] opined that “What moves people to protect bits of nature is a matter of what they have in their minds, what they keep in their hearts, and what they want in their pockets”.
Human history is said to be largely written in terms of the struggle between man and nature over terms of man’s existence [5]. Furthermore for most of human history, the principal threats to man came from nature but today the principal threats to both man and nature come from man himself [6]. Base on the above issue, it has become a growing concern about the state of the environment, and human welfare has assumed a global dimension; the need for concerted and a more focused approach to the management of the environment has not only become imperative but urgent. Presently, there is the growing awareness that concerted socio-economic development requires a compromise between material growth and environmental constraints [7]. The survival of the people in the face of depletion of resources that sustain them hitherto is to adopt a type of development that is friendly or fight against the sort of development that will force them to die or wipe them off the surface of the Earth. The harsh reality and discomfort in the raw material sources nations of the developing or emerging economy somehow affects the destination of the raw material, the developed economy. At this point it is either the earth will burst and civilization cease or something done to save the Earth and mankind. This thinking led to the idea of sustainable development [8].
Sustainable development in this paper is define as a economic development that meets current needs of the people, without compromising the ability of future generation to meet their needs. Precisely, sustainable development is a robust development plan that satisfies the needs of the people at present, without restricting the future generation to enjoy and satisfies their own needs. In a delicate region like Niger Delta, adequate attention and proper action must be taken to sustain the environmental resources especially the biodiversity (which is a product of vegetation resources) and to avoid wastage.Deardenet al. [9]Stated that the relationship among environment, resources, and society is one of the most important challenges, if not the most important challenge, currently facing humanity. For many of Earth’s human inhabitants, this relationship is an on-going reality as they try to meet their everyday needs for food, water, shelter and security. To ignore the relationship is to perish. For others, usually urban and city dwellers, especially in developed countries, the reality seems distant. Food comes from the supermarket, water is piped into homes, even work and home environments have controlled temperature through heating and air conditioning. It is not until disruptions occur in these delivery systems – caused by flood, tsunamis, drought, ice storm, earthquakes, tornadoes, hurricanes, insect infestations or similar forces of nature that many people realize that they too are dependent on the environment for survival as has been true since before the dawn of human civilization.
This study seeks to review the extent of damage done on vegetation resource in the Niger Delta region as a result of unplanned development, and how the remaining resources can be sustained in line with Millennium Development Goals and the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (MDGs and CBS) at the World Earth Summit of 1992.
Vegetation resources include all the resources one can get from the forest and savannah for the benefit of man, animals, plants and the environment. It include timber, roots, leaves, barks of trees, latex, fruits, fibres, firewood, soils, and wild animals [7, 9]. In a tropical zone like Niger Delta the importance of vegetal resources cannot be quantified. It is an institution, tradition and culture and medical store. It warm homes, cook foods and brings money.
Principle of Sustainable Development
Alexander [7] stated that “A clear concept of sustainable development must be known before it can be implemented in any region of the World.” Sustainable development entails three strategic aspects: Vision, Process and Product. It involves a philosophy that deals with vision regarding the nature of future societies. Here attention is given to meeting basic human needs, achieving equity and justice for present and future generation, realizing self-empowerment, protecting the integrity of biophysical systems, integrating environmental and economic considerations, and keeping future options open. It is also a process which emphasizes a system of governance and management characterized by openness, transparency, decentralization and accessibility. According to Dearden and Mitchell [9] it accepts the legitimacy of local or indigenous knowledge and seeks to incorporate such understanding with science based knowledge when developing strategies and plans. It also recognizes that conditions changes and much uncertainty exists. Thus, it is necessary to be flexible and adaptable, thereby allowing for policies and practise to be modified as experiences accumulates.
As product sustainability seeks to ensure that economic, environmental, and social aspects are considered together and that trade-offs are made in a way that is visible and transparent to those affected. Environment is not an inheritance; it is legacy that must be conserved to the next generation.To understand how a vital resource like vegetation should be conserved or sustained for future uses, it is required that issues associated with over exploitation of the resource be recognized and solution proffer.
Problem of sustainability inthe Niger Delta
It is difficult to obey law in the face of hunger and hardship or under oppression and aggression; in any of the above situation what is important is survival.Generally, planning is a recent idea in Nigeria, there is lack of skilled practitioners in urban and regional planning and the foreign trained ones often approached planning problems by using imported development planning models, which in some cases do not work. In Nigeria the first National Development Planning was introduced in 1970. Unfortunately, most often than not, planners have not been given freedom to advance their expertise rather they have been overwhelmed by politicians opinions, resulting to rift between planners and politicians because of differences in perceptions giving rise to frequent changes in strategies in Nigeria [7].
Agriculture, farming and mineral exploitation is the commonest occupation in the Niger Delta region. All the activities in one way or the other affects vegetal resources directly or indirectly. Those in real estate and road construction also affect vegetal resources. The effects of these activities are so pronounced that some animals and vital plant have gone into extinction or near extinction. Human activities on vegetation resources in the Niger Delta region is more glaring than in any other part of Nigeria. Reason being that the area is fragile and terrain prone to changes. Besides, the population that is supported is more than the resources. Aloni, Alexander and Agi-Ottoh[11] noted that agriculture is vital for human existence; however the types of agriculture practice and technology applied could be inimical to both human and the environment. The practice of cutting and burning destroys animals and their habitat, exposes the soil to adverse weather condition, which is responsible loss of soil fertility and erosin.
The earth regenerative capacity can no longer keep up with demand; people are turning resources into waste faster than nature can turn waste into resources. Humanity is no longer living of nature`s interest but drawing down its capital. These growing pressures on ecosystem are causing habitat destruction or degradation and permanent loss of productivity, threatening both biodiversity and human well-being (WWF, 2016).
The Study Area
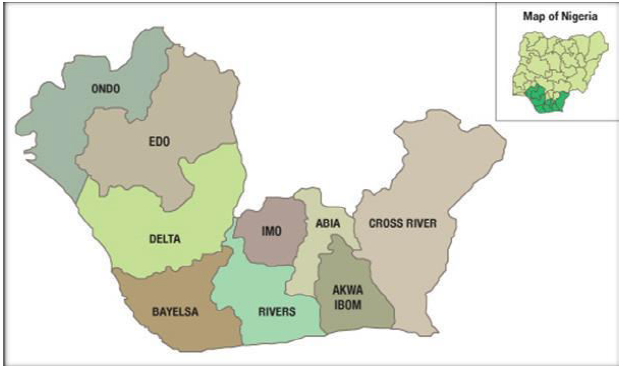
The study is centre around the South –South area of Nigeria known as the Niger Delta region. The area is bordered in the entire South by Atlantic Ocean. It stretches from Benin river estuary for about 450km for twenty one estuaries open and discharges into Atlantic Ocean through the Delta. It consist of major distinct ecological zones such as fresh water, swamp, mangrove, creeks estuaries and barrier island [12]. The Niger Delta region is made up of the core South-South geo-political zone of Nigeria. Politically in the year 2000, Abia, Ondo and Imo State were fused into Oil Mineral Producing Areas Development Commission (OMPADEC) now Niger Delta development commission.Map of the study area is shown in Figure 1 below.
With regard the land mass, contrary to speculation prints, Niger Delta east densely populated region, sometimes called oil rivers because it was once a major producer of palm oil. The area was the British oil rivers protectorate from 1885 until1893, when it was expanded and became the Niger coast protectorate. The Delta is a petroleum rich region, and has been the centre of international controversy over population, corruption, oppression, victimization, marginalization, flood and degradation (www.wikipedia). The Niger Delta presently covers over 70,000Km2 with a population of 21,473,646 persons for the core Niger Delta, and additional 10,209,922 persons for the newly added states ,putting Niger Delta population at 31,683,568 persons, given with the population density of 452.6pers/km2 generally [13].
The mean temperature is about 28°C with relative humidity of about 85% in most of the months, but June, July and September is over 95% and about 65% in December and January.Rainfall type within the region is mostly conventional, and the annual rainfall is over 2500mm. The southern most part record rainfall of about 3000mm, with rainy season stretching over eight (8) months of the year. The inter-tropical discontinuity (ITD) hardly leaves the Niger Delta that explains why rainy season last longer than dry season within the region. The effect of North-East trade wind or the continental air mass presence is short lived around late November to late January. Two dominant soils in Niger Delta are the alluvial and the farrasol[14].The inhabitants of Niger Delta are more than forty (40) ethnic groups which include the Bini, Efik, Esan, Ekpeye, Etche, Ibibio, Ijaw, Ikwerre, Isoko, Itsekiri, Urobo, Ogoni, Ogba,Egbema, Ndoni, Ukwuann among others. The dialect in Niger Delta is over 250, making it the most distinct people in Nigeria (www.wikipedia).
Usefulness of Vegetation Resources
Alexander [7] define vegetation as vital resources derived from the forest or farm land which are often eminence value to man. These include plants and animal (flora and fauna) and soil; their values can be enhanced in form of game reserve, fruits, firewood, latex, fibres, pulps etc.Niger Delta is blessed with good climate and fertile soil; these give rise to robust forest and thick vegetation and biodiversity.Forest resources abound in the area. The abundance of fresh water and salt water give rise to great deal of biodiversity. The presence of thick forest and abundant water within the region ensure that the air quality is high and level of carbon dioxide is minimal. Economic trees like Iroko, Obeche, Mahogany, African Walnut, Opepe, Iron wood (Okwanama) and other hard wood abound and are sources of export and income for Nigeria. The forest also serves bas habitat for wildlife and protection to virgin soils. It is home for source of African traditional medicine. It provides job to thousands of people and serves as research point for researchers. Some forests are sacred spots (religious sites) and cultural shrines. To say that it provides food is a fact that cannot be denied.
Reasonfor expiotation of vegetal resources
Man`s quest to live in an organized society that cares for everything, otherwise known as urbanization have put stress on vegetal resources.Virgin forest in Niger Delta are cleared as site for State headquarters in doing this untold number of trees, wildlife, insects are dislocated. As urban areas open up, roads are built to connect the urban and rural areas, thereby accentuating the depletion of vegetation resources.Industries, firms and institutions are built to service the urban area in expense to vegetation resources.Population pressure is another factor that impact on vegetation resources. As the number of people increases demand for accommodation increases, agricultural land for food provision increases. Schools for the teaming population surface, another service that need to be sited became necessary, all these are threat to vegetation and biodiversity.
Human activities like population, deforestation, poaching, also facilitate depletion on vegetal resources.Oil exploration and pollution in the Niger Delta region has destroyed a lot of forest and wildlife.Lumbering, the practice of felling trees is common within the area. The trees which on its own not standing on a clear stand pull other trees, and most often than not, large vegetation are destroyed before getting the timber out from the forest.Wild fire also destroys vegetation, especially during the dry season. Wild fire could be cause by reckless human activities or thunderstorm. Government policies can as well aggravate the depletion of vegetal resources. For instance if government wish to build a seaport, hospital, research centre, school, stadium, etc., all these will be done on space, which is land, in developing countries virgin forest or vegetation must bear the brunt.Greedy businessmen and politicians have also devastated vegetation in Niger Delta. Waste are dumped in the forest, this is inimical to robust vegetation and water resources.Commercial farming has also led to destruction of original forest by farmers that intend to produce export product that services more of developed economy than Nigeria.
Consequences of depletion of vegetal resources in Niger delta
The study of vegetation depletion affects the environment, biodiversity and human comfort index to mention but a few.Akachukwu [16] stated that Nigeria has the third largest mangrove forest in the world estimated at about 9,730km2. About 10% of the mangrove in the Niger Delta has been lost to urban growth, farming, deforestation and oil exploration and production activities. Similarly, Ogbonnaya [17] reported that Nigeria in 1879 had aout 65 million hectares of intact forest cover, but now has less than 4 million hectares left of which about a third is under effective cover in National parks. It is on record that Nigeria lost 3.7 million hectares of forest between 1981 and 1994 and by 2003; the rate of loss was put at 3.5% annually [15].
The ecological functions and human needs are more threatened in sub-Saharan Africa including Nigeria, and fragile ecosystems such as the Niger Delta in particular [18]. In Nigeria, mangroves occur in inter tidal zones where there are major daily and seasonal fluctuations in water levels (approximately 1 meter). They receive a constant flow of fresh and salt water and are sensitive to reduced fresh water input [19]. He further stated that several activities from oil and gas operations have had direct bearing on the survival of the mangroves. Increases in salinity due to reduced fresh water input or saline water intrusion from canals opening into the sea have caused them to die. They have also been killed by flooding due to the creation of levees through dredging and pipeline trenching.
Many times, there is no consideration for drainage from mangrove areas. Heavy viscous oil kills mangrove by coating and sealing their breathing pores, thereby asphyxiating the subsurface roots that depend on the pores for oxygen. Another danger for mangroves is the molecular weight aromatic compounds that damages root membranes leading to failure of salt control in plant.Anything that affects the mangrove also affects the biodiversity that depend on it. Periwinkle, mudskipper, birds, Red Colobus monkey and pigmy hippopotamus, crabs and even human that depend on mangrove are adversely affected. Depletion of vegetation in the Niger Delta can be clearly seen when we consider biodiversity. Lot of animals, birds, insects, trees are almost gone or gone in some cases. For instance Iron wood that was common can be hardly seen today. The red colobus monkey is now endangered species.
Some animals and plants have gone into extinction, because of human impact on vegetation. When this happens depending on the nature of the species, it is lost in the environment, however if it is an endemic species, it is lost in the entire world.Another negative effect of vegetation depletion is the destruction of traditional medicine and drug. Before the advent of white men there is hardly any sickness or diseases that cannot be taken care of by herbalist, but most of the plants are gone. For instance there are plants the roots and leaves of which clot blood, even when vein is affected. Okafor et al. [20] pointed out that biodiversity maintains our health directly or indirectly. It impact directly through the use of diverse genes and species for biotherapy which our people hold strongly. For example the leaf of SidaAcuta is chewed for treating gonorrhoea. GnetumAfricanum (Okazi) is used for the treatment of diarrhoea and whitlow, AzadirachtaIndica is use for treatment of malaria etc.
Depletion of vegetation also affects rainfall and air quality. Transpiration is the process through which plants lose water to the atmosphere and it occurs in two forms. One, intercepted water is easily lost to the atmosphere. Secondly, the plant loses the water gotten from the soil.In the absence of vegetal resources two things happens;
- The amount of water to beinterceptedwillheat the grounddirectly, thiscaninitiateerosion, excess water on the groundwhichcan lead to runoff, or lead to flood, since the surface isreceiving more water thannecessary.
- Absence of treeswill trigger excessevaporationsince the groundis not undervegetal protection. Excessive evaporationwill lead to abrupt more water moisture, becauseitissudden, itcan trigger windcurrent. Whenthishappened a torrentialrainfallisexpected. This toocanbe destructive or lead to flooding of the area. Theseexplain the more regular incidence of tornadoes and cyclone in Niger Delta region in recent times.
Impact of the neglected symbiotic relationship
Vegetation is a natural check on air pollution. Emitted carbon dioxide are absorbed by vegetation, thereby, reducing atmospheric temperature.What happens in the absence of reduced vegetation is that carbon dioxide accumulates and temperature increases and dust particles cannot be easily absorbed. Leading to urban heat island. This is a situation where urban centres experience higher temperature than the surrounding region. The reason is as a result of depleted vegetation. Industrial centres in rural areas with thick vegetation does not experience urban heat island effect except when the vegetal resources have been poisoned in one way or another (pollution), illegal refining (kpofire) is not new to Niger Delta, though the issue of black soot experience in Rivers state especially Port Harcourt, is as a result of disappearing vegetal resources. Illegal refining is done the forest and is mangrove not under forest mangrove. If it is under thick vegetation the canopy of trees will prevent most of the soot or incomplete particle to get to the atmosphere, it will clot on the leaves. When these trees are used as fuel and pollution kills others, the smoke get to the open and the result is the soot, in more open places like human communities. In the villages, the trees especially in the night absorb high proportion of it.
Worldwide, the quality of vegetal related product like honey has dropped drastically. This is as a result of disturbance and depletion of vegetation, especially for wide honey. Products like mushrooms are also affected. These are local delicacies in Niger Delta. With destruction of forest, low and medium classes cannot afford the artificially cultivated mushrooms.
Remediation
The negative consequences of vegetation depletion in Niger Delta are evidence over human being. It is therefore the responsibility of individuals aware of these dangers to proffer solution to the impact of vegetation depletion in Niger Delta.
- Any attempt to address the impact of vegetal depletion in Niger Delta must have the support of the government. So, strong government legislation and structure is a key to sustainable development in Niger Delta region.There must be laws restricting people, firm, etc. on unwanted vegetal destruction and sanction to defaulters.
- Sustainable agriculture should be practice within the region. This implies that improved crop varieties, use of pesticides, organic manures etc. are used instead of bring new land into production. In developed countries less land have been cultivated now than one hundred years ago in North America or six hundred years ago in Europe [21]. It is on record that 95% of recent agricultural growth in developed countries has come from improved crop varieties rather than increase of land. It has been observed that clearing of more land for agriculture has resulted into tragic losses of biodiversity and valuable ecological services, and physical innovations have been adopted, it has not yield the optimum result.Therefore, sort of agriculture that will lead to improve yield will be encouraged over use of vital resources.
- Discouragement of urban sprawl to reduce the incidence of destroying more vegetation for urban development. Urban sprawl by definition is an urban area with low population density. This type of development will put vegetal resources under pressure. The required land space also endangered the environment. The distance of travelling is costly, and the additional combustion adds to their population. Urban sprawl contributes to loss of, disruption or degradation of adjacent agricultural land, environmentally sensitive areas, natural habitat, and water and air quality. Nucleated and compact settlement should be encouraged. High and tall buildings should be encouraged. Field and parking spaces should be created.
- Environmental Impact Assessment on areas wherereasonable or large amount of vegetalresourcewere to beremoved or colonizedshouldbecarried out in conjunctionwithstakeholdersbeforeremoval. To enhance sustainability of urban buildings, attention shouldbegiven to location and site design. Endangeredspeciesdislodged or destroyed in a swampy, marshy and fragile environmentmay have been destroyed.
- Creation of reserves. The coastalfringes of Niger Delta regionidentified as hotspots of endangered biodiversity should be adopted as gamereserves to savebothanimals and plants. That canalsocreate revenue for the government and encourage tourism, create job for mono-economy states of Niger Delta like Rivers and Bayelsa.
- International laws, treaties, policies and multilateralagreements, conventions and protocolswhich Nigeria is party shouldbehonoured and implemented. Some of the conventions thatneeded urgent implementationinclude Convention on International Trade in EndangeredSpecies of Wild Flora and Fauna (CITES). RAMSAR convention, for Wetland etc.
- The idea of destroyingproduct pipelines for whateverreasonshouldbediscouragedsince the demeritoutweighed the merit. Anyperson or personscaught in the act must be made to face the wrath of the law.
CONCLUSION
Clearing of land for development, may give us job and money to feed our family, but the impact of the environment will kill us and destroy civilization.Human activities emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, without vegetation the atmospheric temperature will but steady increasing. Such will adversely affect agriculture, biodiversity, human activities etc.Prevention is better than cure, so we suggest that green areas should not be encroached, taller building should be encouraged.A robust agricultural system that will reduce falling of trees, destroying of biodiversity should be encouraged, school should introduce green club.
Environmentalist, scholars and concerned members of the communities should protest against wanton destruction of vegetal resources.Vegetal resources are vital in a climate changing environment. No vegetation or little vegetation will lead to increase in many environmental hazards like soot, airborne diseases, flood, drought, wind erosion, etc.Vegetal resources must at least be treated with respect. If not for anything it is the first protection from wind and hiding place in time of war.
REFERENCES
- Todaro MP. Putro TS. Analysis of the Quality of HumanResourcestowards the Millennium Development. Goals of Riau Province in 2015. Journal of Economicsand Sustainable Development.6 (2006): 168.
- Erhun MO. 2015. A SustainableApproach to EconomicDevelopment in Nigeria: A Legal Perspective. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development.6: 1-6.
- Alexander BC. 2016. Lecture Monograph on Agroclimatology, ND 11. CaptainElechiAmadiPolytechnic, Rivers State
- d’Huart JPC. 1999. Stopping the Whirlpool’ People and Planet7: 31.
- Barkley R, Sackler DW. 1972. Economic Growth and Environmentaldelay: The Solution becomes the problems, New York. Harcourt BraceJevonorichInc
- Usoro OE. 1974. Environmental Management and Conservation’Ikhuoria, I.A. (ed). Cartographic Association Woodwell, G.M. ‘Success, Succession and Adam Smith’Bioscience24 (1994): 81-87.
- Arokoyu SB. Emerging Issues in Environmental Management. Bell-Gam WI, Arokoyu SB, Umeuduji JE. Perspective on the HumanEnvironment. Port Harcourt. Amethyst and ColleaguesPublishers (2004).
- Alexander BC. SustainableDevelopment in Fragile Niger Delta Region: A task for environmentalist, International Journal of Development and sustainability 6 (2017): 1239-1304.
- Dearden P, Mitchell B. Environmental Change and Challenge. Oxford UniversityPress, New York (2009).
- 2015. Essential Geography for Senior SecondarySchool. TONAD Pub.Nigeria.
- Aloni C, Alexander BC, Agi-Ottoh C. 2015. The Effect of Unplanned Exploitation of EnvironmentalResources: Nigeria’ Journal of Environmental Pollution and HumanHealth 3: 39-45.
- Ukpong IE. Perspective on Environmental Management. System Club Inc.Uyo, AkwaIbom, Nigeria (2009).
- Nigerian Population Commission. 2006. Nigeria Population Census Report .
- Agola SA. 1979. An Agricultural Atlas of Nigeria. Oxford UniversityPress, London
- Ezeala P. 2003. SavingNigeria’s Forest’ Nature Watch, December: 3.
- Akachukwu AE. 1998. Natural ResourcesUtilization and Environment, Paper presented at 10th Annual Workshop of NEST, Abia State
- Ogbonnaya O. 2003. Deforestation in Nigeria; Consequences and Solution’ Nature Watch, December: 6-7.
- Phil-Eze PO, Umeuduji JE. 2004. Human Impact on Biodiversity, Bell-Gam WI, Arokoyu SB, Umeuduji JE. Perspectives on the HumanEnvironment. Port Harcourt. Amethyst and ColleaguesPublishers
- Azaiki S. 2007. Oil, Gas, and Life in Nigeria. BoksAuthoprint, Ibadan, Nigeria
- Okafor JC, Ham R. 1999. Identification, Utilization and Conservation of Medicinal Plants in South Eastern Nigeria. Issues in AfricanBiodiversity. BSP:3.
- Cunningham WP, Saigo BW. 1997. Environmental Science – A Global Concern, 4th Edition, McGraw-Hill Pub. New York

 Impact Factor: * 3.6
Impact Factor: * 3.6 CiteScore: 2.9
CiteScore: 2.9  Acceptance Rate: 11.01%
Acceptance Rate: 11.01%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 