The Distribution Properties of Two-Parameter Exponential Distribution Order Statistics
Roland Forson1*, Cai Guanghui1, Samuel Ofori2, Oo Than Nweit2, Daniel Ofori Kusi3
1Department of Statistics and Mathematics, Zhejiang Gongshan University, China
2Department of Mathematics and Physics, Zhejiang Normal University, China
3Department of Mathematics, University of Free State, South Africa
*Corresponding Author: Roland Forson, Department of Statistics and Mathematics, Zhejiang Gongshan University, China
Received: 25 April 2019; Accepted: 04May 2019; Published: 10 May 2019
Article Information
Citation: Roland Forson, Cai Guanghui, Samuel Ofori, Oo Than Nweit, Daniel Ofori Kusi. The Distribution Properties of Two-Parameter Exponential Distribution Order Statistics. Journal of Analytical Techniques and Research 1 (2019): 003-009.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
This paper proposes the distribution function and density function of double parameter exponential distribution and discusses some important distribution properties of order statistics. We prove that random variables following the double parameter exponential type distribution X1, X2,..., Xn are not mutually independent and do not follow the same distribution, but that the Xi, Xj meet the dependency of TP2 to establish RTI ( Xi | Xj ), LTD (Xi | Xj ) and RSCI.
Keywords
<p>Order statistics, Double parameter exponential distribution, TP2, RTI, LTD, RSCI</p>
Article Details
1. Introduction
In this paper, some important properties of order statistics of two-parameter exponential distribution are discussed when the distribution and density functions of a two-parameter distribution is given. We also proved that the random variables X1, X2,..., Xn, obeying the two-parameter exponential distribution are not independent of each other, and do not obey the same distribution. Order statistics is a kind of statistics distribution commonly used in statistical theory and application of which there are many research [1-6]. The two parameter exponential distribution is also a very useful component in reliability engineering. This study considers the nature of order statistics. Its density function and distribution functions are respectively [7];
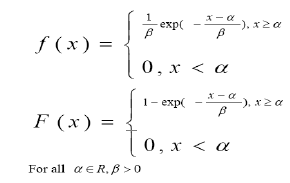
2. Prerequisite Knowledge
2.1 Lemma 1
Let all X follow a continuous distribution function F (x) and its density function of F (x), {a < x < b}, X1, X2,...Xn is a simple random sample with acapacity of N from X2
- The joint probability density function of (X1, X 2,..., X n) if a ≤ X1 < X 2 < ... < Xn ≤ b is

Otherwise,
g1,2,...,n ( X1, X 2, ..., X n ) 0
- The joint probability density function of order statistic (Xi, Xj )(1 ≤ I ≤ j ≤ n) is a ≤ x ≤ y ≤ b and
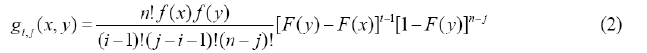
Otherwise,
gi, j (x, y) 0
- The probability density function of order statistics X (k) is
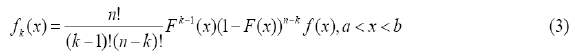
In particular, when k = 1, there is

When k = n, there is

2.2 Lemma 2
Assume that X and Y are two random variables, the joint probability is f (x) if the inequality x1 ≤ x2, y1≤ y2 is satisfied [10].
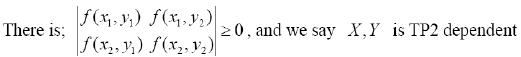
2.3 Lemma 3
For a fixed x, y, if P (X > x, Y > y | X > x1, Y > y1 ) is a monotonic increasing function for variables x1 and y1, then variables X, Y satisfies RSCI [10] .
2.4 Lemma 4
For any y1, if P (Y ≤ y1| X ≤ x1 ) is monotone decreasing function of x1, then Y is the left tail decreasing function of X, denoted by Ltd ( XY ) [11].
2.5 Lemma 5
For any y1, if P (Y > y1 | X > x1 ) is an incremental function of x1, then Y is the right tail growth of X, denoted by RTI (XY) [11].
3. Main Conclusion
3.1 Theorem 1
Let the total X follow a continuous distribution function of F (x) and its density function F (x) (a < x < b), X1, X2,..., Xn be a simple random sample with a capacity of N from the population X, and X1, X2,..., Xn
- The order statistics of the joint probability density function of (X1, X2,..., Xn ) is as follows; a ≤ X1 2 < ... n ≤ b
If then
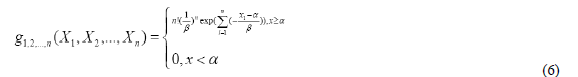
- The probability density function of X k is;
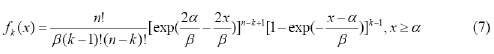
In particular, when k 1, there is

When k= n,
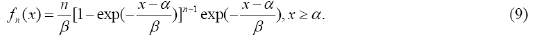
Which is proved from lemma 1.
3.2 Theorem 2
If X1, X2, ..., Xn is independent of each other and obeys a two-parameter exponential distribution, then X1, X2, ..., Xn is not independent of each other and does not obey the same distribution.
Proof : Let n = 2 be used to represent the observations of x1 and x2 with X1 and X2 respectively. It can be seen from lemma 1 that the density function of (X1, X2) is
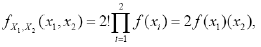
The density functions of X1 and X 2 are respectively
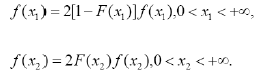
Assuming that X1 and X 2 are independent, then fX1,X 2 (x1, x2 ) = f (x1 ). f (x2 ), and 2 f (x1 ) f (x2 ) = 2[1- F (x1)] f (x1).2F (x2 ) f (x2 ) = 4 [1-F (x1 )]F (x2 ) f (x1 ) f (x2 ).
Therefore,
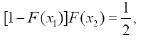
Then,
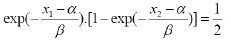
Which obviously does not hold. So
f X1, X 2 (x1, x2 ) ≠ f (x1 ). f (x2)
Therefore, X1 and X 2 are not independent of each other and do not obey the same distribution. Hence proved.
3.3 Theorem 3
If X1, X2,..., Xn are independent of each other and obey the two-parameter exponential distribution, then X i,Yj (I < j) is TP2 dependent.
Proof: The observations of xi and xj are represented by Xi, Xj. For any xi < xj, the joint density function of Lemma 1, is
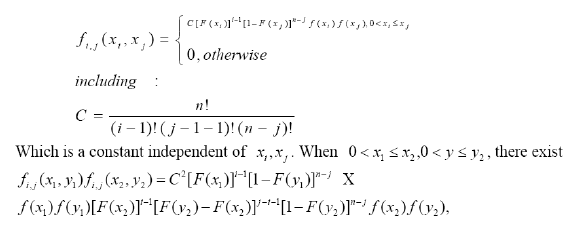
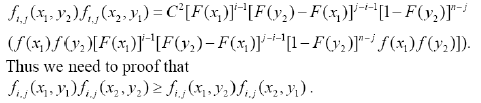
We only need
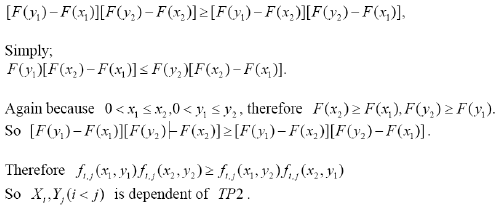
3.4 Theorem 4
Suppose X1, X2, ..., Xn is n independent and identically distributed random variables from the exponential distribution of two parameters, then RTI (Xj | Xi), i< j. It is proved that for any s, t when s > t, there is
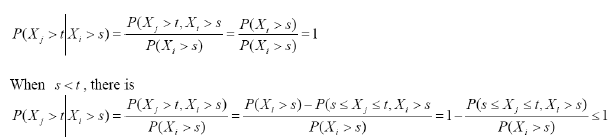
When it is fixed and so increases. The integral of P (≤ Xj ≤ t, Xs) decreases P(s ≤ Xj ≤ t, Xi > s)
P (Xj > t | Xi > s) LTD( Xi | Xj), i < j according to the density functions becomes smaller and becomes larger.
3.5 Theorem 5
Suppose Xi and Xj are two random variables independently obeying the same two-parameter exponent. Then X1 and X2 satisfy RCSI (i.e for fixed X and Y and Y, if P (X x,Y y | X x ', Y y' ) is a monotonic increasing function of variables x' and y', it is proved that the joint density functions of X1 and X2 is f1,2 (x1, x2). When x1, x2 is invariant, P( X1 > x1, X2 > x2 | X1 > x'1, X2 > x'2 ), x'1, x'2 is increasing function

iii When x1 < x'1, x2 > x'2 or x1 > x'x, x2 < x'2 are equally available,
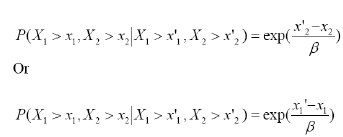
When x1, x2 are fixed, they are incremental functions of x'1, x'2. In conclusion, P( X1 > x1, X2 > x2 | X1 > x'1, X2 > x'2) are incremental functions of x1 ', x'2. So X1, X2 satisfies RSCI.
4. Conclusion
Some distribution properties of order statistics obeying two-parameter exponential distribution are discussed. It is proved that when X1, X2,..., Xn are independent of each other and obey the exponential distribution of two-parameters, the order statistics X1, X2, ..., Xn is not independent of each other and does not obey the same distribution, but Xi, Xj satisfies TP2 dependence. For any i < j, there are RTI ( Xj | Xi ), LTD( Xi | Xj), and X1, X2 that satisfy RSCI.
References
- He Jia, Du Chaoxiong. On the Sequencial Satistical Distribution Properties of Exponential Distribution. Journal of Hunan University of science and technology: Natural science edition 26 (2011): 125-128.
- Jiang Penihua. Distribution properties of Weibull distribution order statistics. Anqing Normal University: NaturalScience Edition 18 (2012): 47-50.
- Kuang Nenghui. The Distribution Properties Two-parameter Rayleigh Distribution Sequencial Statistics. Journal of Jianxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition 33 (2009): 648-651.
- Kuangneng Hui. Distribution Properties of Laplace Distribution Sequence. Journal of Xuzhou Normal University: Natural Science Edition 27 (2009): 34-37.
- Kuangneng Hui. The Distribution properties of Gamma Distribution order statistics. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology 13 (2010): 17-19.
- Xiong Jiabing, Wang Zhixing. Properties of Uniform Distribution orderStatistics. Advanced mathematics research 13 (2010): 17-19.
- Liu Xuan. Accurate formula for calculating the minimum and maximum moments of ordinal statistics of exponential distribution with two parameters. Journal of Zhengzhou University: Science Edition 47 (2015): 41-44.
- Wang Wei. A Proof of the Distribution Sequential Statistics. Journal of Changchun University 12 (2002): 20-21.
- He Chaobing, Tian Yanwei. Distribution of Sequential Statistics. Journal of Chengdu University.. Natural Science Edition 27 (2008) : 116-119.
- Jin Liqin. Statistical Characteristics of Index Distribution and Geometric distribution. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University (2013).
- Ave’rous J, Dortet-Bernadet JL. LTD and RTD dependence ordering. Canadian Journal of Statistics 28 (2000): 15-157.


 Impact Factor: * 2.8
Impact Factor: * 2.8 Acceptance Rate: 77.30%
Acceptance Rate: 77.30%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 