Personalized Medicine in Woman Lung Cancer: Crizotinib and Osimertinib Association to Overcome Osimertinib Resistance
Fanny Leenhardt1,2*, Marie Viala3, Stephane Pouderoux3, Pierre Boisselier4, Xavier Quantin2,3
1Pharmacy Service, Montpellier Cancer Institute, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France
2Montpellier Cancer Research Institute (IRCM), University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France
3Department of Medical Oncology, Montpellier Cancer Institute, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France
4Department of Radiotherapy Oncology, Montpellier Cancer Institute, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France
*Corresponding author: Fanny Leenhardt, Pharmacy Service, Montpellier Cancer Institute, University of Montpellier, 208 rue des Apothicaires, 34298, Montpellier, France
Received: 26 May 2020; Accepted: 10 June 2020; Published: 01 July 2020
Article Information
Citation:
Fanny Leenhardt, Marie Viala, Stephane Pouderoux, Pierre Boisselier, Xavier Quantin. Personalized Medicine in Woman Lung Cancer: Crizotinib and Osimertinib Association to Overcome Osimertinib Resistance. Journal of Women’s Health and Development 3 (2020): 154-157.
DOI: 10.26502/fjwhd.2644-28840028
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the second most diagnosed cancer in women. Research on this type of cancer has benefited from the development of precision medicine for several years. In this case study, elderly women was treated for an advanced NSCLC with brain localization and who has been treated by novel association, osimertinib and crizotinib, in front of dual mutation (EGFR and CMet). This combination of targeted therapies succeeded to partial response on primary lung tumor and total reduction on brain metastasis.
Keywords
<p>Lung cancer; Oncogenetic somatic; Women health; Targeted therapy</p>
Article Details
Introduction
Lung cancer in women has been steadily increasing since the 1960s. This can mainly be explained by the increase in
smoking behavior among women [1]. Lung cancer in nonsmokers is the sixth most common cause of cancer death for women in the US. Among women who never smoke, nearly half of them present an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) mutation. Until recently, first- or second-generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKI) were the recommended treatment. For this type of treatment, when treatment failure occurs (median time to progression 10 to 12 months), it is due – for more than half of the cases - by the addition of a T790M mutation. This mutation confers resistance but third generation TKI (osimertinib) can overcome it. The median progression free survival after introduction of osimertinib is around 12 months. Various mechanisms may explain disease progression under osimertinib but until now chemotherapy is the recommended option in this situation. A better comprehension of the mechanisms of disease progression may offer new opportunities of treatment. Among these mechanisms, MET amplification can explain 5 to 20 % of tumor progression. Crizotinib a TKI against ALK, ROS and MET may overcome resistance in combination with osimertinib. In this case study, we focused on a woman who developed under second line osimertinib a MET amplification and achieved disease control with the combination of full dose osimertinib and crizotinib.
2. Case Presentation as Materials & Methods and Results
This is a 71 years old woman who was diagnosed with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The disease involved the left lower lobe, pleura and multiple cerebral metastases. Molecular analysis was performed on primary tumor biopsy and revealed EGFR Del19mutation. Afatinib was introduced and permitted to obtain a Partial Response. After almost 2 years of treatment with afatinib (from January 2017 to November 2018), clinical progression was observed leading to chemotherapy treatment (Carboplatin + Pemetrexed, four cycles) in November 2018. The occurrence of renal failure, platinium salts mediated, limited the continuation of the treatment beyond the first cycle. A completed molecular analysis on liquid (DNAct) and tumor biopsy was performed and highlighted EGFR mutation, Del19, on both types of biopsy. Afatinib was reintroduced in June 2019. Therapeutic afatinib monitoring highlighted an biological optimal drug exposition, 23 ng/mL at plasma trough concentration [2]. Good control of the disease at the brain level was observed but the left lower lobar mass was progressing (Figure 1). A novel tumor biopsy revealed exon 14 cMet amplification and EGFR T790M additional mutation and afatinib was switched for osimertinib in September 2019. After 3 months of treatment, radiologic evaluation (scanner and IRM) have confirmed osimertinib effectiveness with neuro-meningeal regression and a patient performans status improvement. However, the disease progressed in the lungs and new lesions appeared on adrenal gland and extensive intra-abdominal lymphadenopathy. Given the cMET amplification evidence on lung biopsy, it was therefore decided to consider osimertinib and cMet inhibitor, crizotinib, dual therapy in January 2020. After 2 months of treatment, radiologic evolution showed a complete response on brain metastasis, regression of lung disease and stabilization of the disease otherwise (Figure 1). Three months before starting this combination of treatment, the patient had language and balance problems which are fully resolved now as the CNS metastasis regressed.
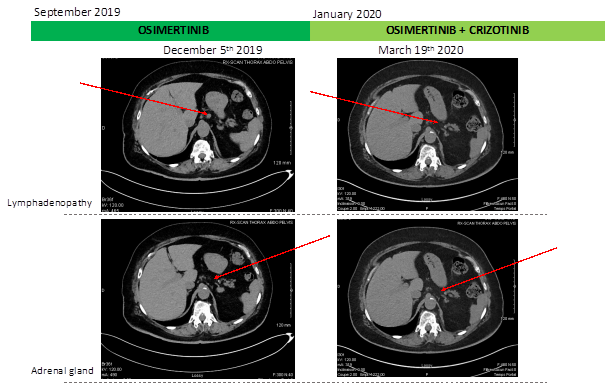
Figure 1: Schematic summary of treatment course and radiologic evolution of lymphadenopathy and adrenal gland during treatment.
For our patient with advanced NSCLC with CNS localization, association of crizotinib and osimertinib have modified the patient's poor prognosis and lead to a complete response on brain metastasis with partial response in lung localization. This has been made possible by routine clinical research into specific molecular variants of lung cancer (EGFR pathway, cMet, Alk, …). Occurrence of cMet mutation or coexisting of T790 mutation and cMet amplification is very rare with 3% of occurrence on NSCLC but already known as EGFR inhibitor biomarker of therapeutic escape (5-20% of case) [3, 4]. No targeted therapies are FDA or EMA approved to target MET amplification, but crizotinib has demonstrated in vitro and in vivo efficacy [5]. Comprehensive genomic profiling can lead to novel approach of cancer treatment and a personalized medicine in oncology. One-third of EGFR mutant NSCLC develop CNS metastasis [6]. Osimertinib has improved blood-brain-barrier penetration and its activity against brain metastasis has been demonstrated in AURA and FLAURA study [7, 8], and confirmed for this patient. A retrospective nationwide population-based cohort study in South Korea highlighted that female sex is a factor associated with subsequent brain metastasis in NSCLC [9]. Nevertheless, female sex was a prevalent factor to long-term survival of lung cancer with brain metastasis [10]. This elderly patient had benefited of a treatment tailored to her pathology and genomic profile at full dosage and optimal tolerance. Age does not appear to be a limiting factor of targeted therapies treatment. Despite the effectiveness of the osimertinib and crizotinib combination, it is now necessary to evaluate its efficacy and safety in prospective clinical trials.
Acknowledgements
Laboratoire de Biochimie et Biologie moléculaire, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nîmes, France for afatinib plasma monitoring
Conflicts of Interest
No Conflicts of interest for all authors
References
- Weir HK. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975-2000, Featuring the Uses of Surveillance Data for Cancer Prevention and Control. Cancer Spectrum Knowl Environ 95 (2003): 1276-1299.
- Yang JC-H, Sequist LV, Zhou C, Schuler M, Geater SL, Mok T, et al. Effect of dose adjustment on the safety and efficacy of afatinib for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma: post hoc analyses of the randomized LUX-Lung 3 and 6 trials. Ann Oncol 27 (2016): 2103-2110.
- Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, et al. Analysis of Tumor Specimens at the Time of Acquired Resistance to EGFR-TKI Therapy in 155 Patients with EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers. Clin Cancer Res 19 (2013): 2240-2247.
- Baldacci S. Conséquences de la dérégulation de MET sur le phénotype des cancers bronchiques non à petites cellules EGFR mutés devenus résistant aux inhibiteurs de tyrosine kinase d’EGFR (2017).
- Yakes FM, Chen J, Tan J, Yamaguchi K, Shi Y, Yu P, et al. Cabozantinib (XL184), a Novel MET and VEGFR2 Inhibitor, Simultaneously Suppresses Metastasis, Angiogenesis, and Tumor Growth. Mol Cancer Ther 10 (2011): 2298-2308.
- Kelly WJ, Shah NJ, Subramaniam DS. Management of Brain Metastases in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol 8 (2018): 208.
- Abdallah SM, Wong A. Brain metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer: are tyrosine kinase inhibitors and checkpoint inhibitors now viable options?. Curr Oncol 25 (2018): S103-S114.
- Liam C-K. Central nervous system activity of first-line osimertinib in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Transl Med 7 (2019): 61-61.
- Lee JS, Hong JH, Sun DS, Won HS, Kim YH, Ahn MS, et al. The impact of systemic treatment on brain metastasis in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective nationwide population-based cohort study. Sci Rep 9 (2019): 18689.
- Niemiec M, Glogowski M, Tyc-Szczepaniak D, Wierzchowski M, Kepka L. Characteristics of long-term survivors of brain metastases from lung cancer. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 16 (2011): 49-53.


 Impact Factor: * 3.4
Impact Factor: * 3.4 Acceptance Rate: 78.89%
Acceptance Rate: 78.89%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 