Outcomes of Lumbar Disc Herniation Treatment using Medication Method Coupled with Epidural Hydrocortisone Injection
Thanh-Hoang Nguyen and Quang-Tri Lê*
Department of Orthopaedics, 7A Military Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
*Corresponding Author: Quang-Tri Le, Head of Department of Orthopaedics, 7A Military Hospital,
466 Nguyen Trai Street, Ward 8, District 5, Ho Chi Minh City, 72706, Vietnam
Received: 30 December 2019; Accepted: 06 January 2020; Published: 07 January 2020
Article Information
Citation: Thanh-Hoang Nguyen, Quang-Tri Lê. Outcomes of Lumbar Disc Herniation Treatment using Medication Method Coupled with Epidural Hydrocortisone Injection. Journal of Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine 2 (2020): 1-9.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Background: Evaluation of lumbar disc herniation treatment outcome using medication method coupled with epidural hydrocortisone injection.
Methods: Description, clinical experiment with the control group, supervision, and evaluation on 62 patients before treatment, 15 days after surgery and 30 days after treatment, in 7A Military Hospital (Ho Chi Minh City, VietNam) from November 2015 to June 2016. Group I (control) included 31 patients treated with essential medication. Group II (experiments) included 31 patients treated with essential medication plus lumbar epidural injection.
Results: At 30 days after treatment 48.4% experiment patients reported no pain (in comparison with 32.3% control ones), 67.7% experiments reported improvement in lumbar flexion (38.7% controls), 64.5% experiments reported great improvement in Lasegue test (38.7%). Flexion, extension, adduction, and rotation were significantly better improved in experiments than in controls. Daily function improvement in experiments (58.1%) was sharply better than controls (19.4%). In general, 80.7% experiments got “very good” treatment outcome, compared with 67.7% controls.
Conclusions: The experiment group got significantly better treatment outcomes than the control group.
Keywords
<p>Disc herniation; Lumbar spinal cord; Epidural injection</p>
Article Details
1. Introduction
Disc herniation is a situation when the spinal disc nucleus is pushed out of the annulus due to a tear or rupture in the annulus and presses on spinal nerves. Herniation in the lumbar causes 63-73% of back pain cases and 72% of sciatica, which seriously affects life quality, social and labor activities of the patients [1-6]. Sciatica with or without lumbar pain makes up 11.5% cases treated at the Department of Musculoskeletal System in Bach Mai Hospital (Ha Noi, Viet Nam) from 1991 to 2000 [7]. Epidural hydrocortisone injection was mentioned in 1952 as a pain relief for lumbar herniated disc sciatica patients [8, 9]. The clinical protocol applied in the 7A Military Hospital for this situation was medication coupled with epidural steroid injection; no detailed research was done to evaluate treatment results, though. Therefore this study was carried out for evaluation of lumbar disc herniation treatment outcome using medication coupled with epidural hydrocortisone injection.
2. Methods
2.1 Research targets
Sixty-two patients diagnosed with lumbar disc herniation at the Department of Orthopaedics, 7A Military Hospital.
2.1.2 Chosen criteria
- Patients with typical clinical sciatic nerve pressure.
- Subclinical: Patients with lumbar disc herniation MRI images.
2.1.2 Rejection criteria
- Disc herniation patients treated with surgery.
- Patients with structural scoliosis.
- Patients being allergic to palliative or anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Migrated disc herniation patients.
- Patients with cauda equina syndrome.
- Non-volunteers or patients did not follow the treatment protocol.
2.2 Research methods
Descriptive research method coupled with clinical experiments with a control group.
2.2.1 Data collection
Case-by-case prospective analysis research.
2.2.2 Random and simple sampling
Diagnosed lumbar herniated disc patients were divided into two groups with similar age, sexes, careers, geography:
- Group I (control) included 31 patients treated with basic medication (Nivalin 2.5mg x 2 vials/day, IM injection; Nucleoforte 1 vial/day, IM injection. Methycobal x 1 vial/2 days. Mobic 7.5mg x 2 tablets/day, P.O.. Myonal 50mg x3 tablets/day, P.O.. Paracetamol 0.5g x 2 tablets/day, P.O.).
- Group II (experiment) included 31 patients treated with essential medication coupled with NMC CSTL injection (Hydrocortisone 125mg x 1 vial/injection, three injections, one injection every five days).
2.3 Research contents
Patient medical history, clinical examination results, health development from before treatment to 15 days, and 30 days after surgery were recorded in a standard form.
2.3.1 The traits of researched patients are list as follow
- Age was divided into four categories (below 30, 30 to 49, 50 to 69 and above 70 years old).
- Sexes: male and female groups.
- Career: heavy workload (workers, farmers …) and light workload groups (officials, pensioners…).
- Contraction duration: under one month, 2 to 5 months, over six months.
- Causes: (1) natural causes, (2) post-trauma, and (3) excessive movement in the wrong posture.
2.3.2 Treatment outcomes were evaluated based on criteria of Nguy?n V?n Thông (1993) [10].
- Back pain and sciatica level based on patient declaration using VAS scale (no pain: 0 point, slight pain: 1-2.5 points, moderate pain: 2.5- 5 points, severe pain: > 5 points).
- Measurement of lumbar flexion using Schober test (Very good/4 points ≥ 14/10cm, Good/3 points ≥ 13/10-14/10cm, Average/2 points ≥ 12/10-13/10cm, Poor/1 point < 12/10cm).
- Measurement of pressure on sciatic nerve roots using Lasegue test (Very good/4 points > 800, Good/3 points ≥ 60-800, Average/2 points ≥ 30-600, Poor/1 point < 300).
- Movements of the lumbar spinal cord (Flexion, extension, adduction toward pain and non-pain sides, rotation toward pain, and non-pain sides).
- Daily functional activities: using “Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire” to evaluate activities of personal care, heavyweight lift, walking and standing (Very good: 4 points, Good: 3 points, Average: 2 points, Poor: 1 point).
- Total accumulated scores assessment: Very good: 36-40 points, Good: 30-35 points, Average: 20-29 points, Poor: <20
2.4 Data analysis
Using SPSS 16.0. Software.
3. Results
3.1 General traits of patients
- Average ages are 57.26 (control) and 58 (experiment). Thirty-six patients belonged to age 50-69 (58%), most of them in age 60-69 (35.5%) and 50-59 (22.5%).
- Females made up of 80.65% of the patients, four times higher than males (19.35%).
- The light workload group took accounted for 5% of the patients, 1.8 times higher than the heavy workload (35.5%).
- Early treatment (within the first month of illness) took 33.8%, the ones begin treatment at 2nd to 5th month took 41.9% and 6th to 12th month gained 24.3%.
- Natural cause accounted for the most significant percentage, then excessive movement and wrong posture. Trauma accounted for no investigated case.
- Moderated herniated disc took the most considerable portion of 88.7%; light one took 11.3%.
- Herniation occurred mostly at disc L4-L5 L5-S1, then were the case of multilevel herniation.
3.2 Treatment outcomes
The pain level decreased remarkably in both control and experiment groups at 1 and 3 months after treatment. Slight pain and no pain percentage in the experiment group were significantly higher than in the control group (p < 0.05) (Table 1).
|
Group |
Controls (n=31) |
Experiments (n=31) |
||||||||||
|
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
|||||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
Severe pain |
20 |
64.5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
18 |
58.1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Moderate pain |
10 |
32.3 |
18 |
58.1 |
6 |
19.4 |
11 |
35.5 |
10 |
32.3 |
3 |
9.7 |
|
Slight pain |
1 |
3.2 |
10 |
32.3 |
15 |
48.4 |
2 |
6.5 |
14 |
45.2 |
13 |
41.9 |
|
No pain |
0 |
0 |
3 |
9.7 |
10 |
32.3 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
22.6 |
15 |
48.4 |
Table 1: Pain relief after treatment (using the VAS scale).
Lasegue sign was remarkably improved in both groups after treatment (p < 0.05), and improvement in experiments was significantly higher than in controls (p < 0.05) (Table 2).
|
Extent |
Controls (n=31) |
Experiments (n=31) |
||||||||||
|
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
|||||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
Very good |
0 |
0 |
11 |
35.5 |
12 |
38.7 |
0 |
0 |
18 |
58.1 |
20 |
64.5 |
|
Good |
9 |
29 |
11 |
35.5 |
13 |
41.9 |
11 |
35.5 |
8 |
25.8 |
8 |
25.8 |
|
Average |
5 |
16.1 |
9 |
29 |
6 |
19.4 |
4 |
12.9 |
5 |
16.1 |
3 |
9.7 |
|
Poor |
17 |
54.8 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
16 |
51.6 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Table 2: Lasegue sign improvement after treatment.
Lumbar flexion was remarkably improved in both groups after treatment (p < 0.05), and improvement in experiments was significantly higher than in controls (p < 0.05) (Table 3).
|
Extent |
Controls (n=31) |
Experiments (n=31) |
||||||||||
|
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
|||||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
Very good |
1 |
3.2 |
11 |
35.5 |
12 |
38.7 |
1 |
3.2 |
20 |
64.5 |
20 |
67.7 |
|
Good |
9 |
29 |
8 |
25.8 |
11 |
35.5 |
8 |
25.8 |
5 |
16.1 |
5 |
16.1 |
|
Average |
7 |
22.6 |
10 |
32.3 |
8 |
25.8 |
8 |
25.8 |
6 |
19.4 |
6 |
19.4 |
|
Poor |
14 |
45.2 |
2 |
6.5 |
0 |
0 |
14 |
45.2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Table 3: Lumbar flexion after treatment (Schober test).
Daily functions in both groups remarkably improved after treatment (p < 0.05), and improvement in experiments was significantly higher than in controls (p < 0.05) (Table 4).
|
Extent |
Controls (n=31) |
Experiments (n=31) |
||||||||||
|
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
Pre-treatment |
15 days after treatment |
30 days after treatment |
|||||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
Very good |
0 |
0 |
2 |
6.5 |
6 |
19.4 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
22.6 |
18 |
58.1 |
|
Good |
2 |
6.5 |
17 |
54.8 |
18 |
58.1 |
1 |
3.2 |
19 |
61.3 |
9 |
29 |
|
Average |
7 |
22.6 |
10 |
32.3 |
6 |
19.4 |
8 |
25.8 |
5 |
16.1 |
4 |
12.9 |
|
Poor |
22 |
7.1 |
2 |
6.5 |
1 |
3.2 |
22 |
71 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Table 4: Daily functions improvement after treatment.
After 15 days, both groups achieved good results and no patient had a poor outcome. Treatment outcome in experiments was significantly higher than in controls (p < 0.05). After 30 days, operations also get substantially better result than controls (p < 0.05) (Table 5+6) and (Figure 1).
|
OUTCOME (15 days) |
Controls (n=31) |
Experiments (n=31) |
P |
||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
||
|
Very good |
0 |
0 |
5 |
16.1 |
<0.05 |
|
Good |
10 |
32.3 |
16 |
31.6 |
|
|
Average |
21 |
67.7 |
10 |
32.3 |
|
|
Poor |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Very good |
31 |
100 |
31 |
100 |
|
|
OUTCOME (30 days) |
Controls (n=31) |
Experiments (n=31) |
p |
||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
||
|
Very good |
8 |
25.8 |
15 |
48.4 |
<0.05 |
|
Good |
13 |
41.9 |
10 |
32.3 |
|
|
Average |
10 |
32.3 |
6 |
19.3 |
|
|
Poor |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Very good |
31 |
100 |
31 |
100 |
|
Table 5 and 6: General treatment outcome (based on criteria of Nguy?n V?n Thông) [10] 15 days and 30 days after treatment.
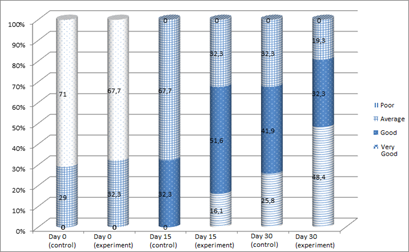
Figure 1: Treatment outcome by time.
4. Discussion
4.1 General traits of investigated patients
The average patient age in this study was 58.16 ± 13.7, suitable with the work of Nguyen et al. (2016) [11], (54 ± 11.04) and higher than other authors such as Davis (1994) (42 years old) [12]. The illness was at a higher rate in females due to heavy workload, and due to, in most cases, menopause age which caused various changes in hormone level lead to spinal disc degeneration and osteoporosis, increased herniation rate. Light workload patients took a majority in this study, different from other studies such as of Nguyen et al. (2016), [11] where 60.0% of the patients did heavy labor. Most patients in our study are in patients hospitalized in the Department of Orthopaedics of the 7A Military Hospital and are mainly pensioners. In this study, the early treatment (within the first month of illness) took 33.8% of the total patients; the ones begin treatment at 2nd to 6th month took 41.9% later than 6th month took 13.3% and at least from the 6th month took 24.3%. Natural causes accounted for the most significant part of investigated patients (47 people, 75.8%), which meant constant work/movements in several limited postures, chronic trauma, osteoporosis and degenerated body structure together contributed to the natural cause of this illness. MRI results of the herniated disc in this study also similar to other researches.
4.2 Treatment results of investigated patients
Nguyen and Phan and until 1997 treated 1390 sciatica cases caused posteriorly herniated disc at semi acute-chronic stage using spinal reduction, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers, epidural injection; 80% cases yielded good and fair results, 13% yielded an average, 4% yielded poor and 3% yielded none result [13]. Riew et al. (2000) reported that one prospective study on severe sciatica cases caused by spinal stenosis or lumbar disc herniation treated with lumbar NMC steroid injection yielded success rate of 77 % [14]. Runu et al. (2005) made a prospective study on treatment of sciatica patients caused by lumbar disc herniation using NMC steroid injection, showed that 72.54% of patients got better [15]. This study result was believed to be similar to the abovementioned works.
5. Conclusion
The studied treatment method did improve spinal range of motion, daily functions, and relieving pain as:
- 4% experiment patients no longer feel pain after treatment (32.3% in the control group).
- Lumbar flexion was significantly improved in 67.7% experiment patients (38.7% in the control group).
- Lasegue score was very good in 64.5% experiment patients (38.7% in the control group).
- Flexion, extension, adduction, and rotation were significantly better improved in experiments than in controls.
- Daily functions were improved at a “very good” extent in 58.1% of experiment patients (19,4% % in the control group).
- General assessment after 30 days: 7% of patients received epidural injection got “very good” outcome compared with 67.7% in the control group.
Funding
None
Conflict of Interest
None declared
Ethical approval
Not required
References
- Ament J, Thaci B, Yang Z, et al. Cost-effectiveness of a bone-anchored annular closure device versus conventional lumbar discectomy in treating lumbar disc herniations. Spine 44 (2019):5-16.
- Deyo RA, Cherkin D, Conrad D, et al. Cost, controversy, crisis: low back pain and the health of the public. Annu Rev Publ Health 12 (1991): 141-156.
- Engel-Yeger B, Keren A, Berkovich Y, et al. The role of physical status versus mental status in predicting the quality of life of patients with lumbar disk herniation. Disabil Rehabil 40 (2018): 302-308.
- Legrand E, Bouvard B, Audran M, et al. Spine Section of the French Society for Rheumatology. Sciatica from disk herniation: medical treatment or surgery? Joint Bone Spine 74 (2007): 530-535.
- Patel SA, Wilt Z, Gandhi SD, et al. Cost-effectiveness of treatments for lumbar disc herniation. Seminars in Spine Surgery 28(2016): 53-56.
- Sardaru D, Boldureanu D, Andruseac G, et al. Paralytic Lumbar Disc Herniation. A Four Years Social and Economic Impact Study for North-East Region of Romania. Rev Cercet Interv So : 67-77.
- Tran N.A and Nguyen TNL. ?au th?n kinh t?a do thoát v? ??a ??m c?t s?ng th?t l?ng. In: B?nh h?c N?i khoa T?p 1, Nhà xu?t b?n Y h?c 2004: 456-460.
- Botwin K, Brown LA, Fishman M, et al. Fluoroscopically guided caudal epidural steroid injections in degenerative lumbar spine stenosis. Pain Physician 10 (2007): 547-558.
- Collighan N, Gupta S. Epidural steroids. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain 10 (2009): 1-5.
- Nguyen VT, Góp ph?n nghiên c?u và ?ánh giá xoa bóp n?n ch?nh c?t s?ng ?i?u tr? thoát v? c?t s?ng th?t l?ng, Lu?n v?n Ti?n s? khoa h?c Y h?c, H?c vi?n Quân Y (1993).
- Nguyen TNL, ?ao XT, ?o VA, et al. ?ánh giá hi?u qu? ?i?u tr? ?au th?n kinh to? do thoát v? ??a ??m b?ng ph??ng pháp tiêm corticosteroid ngoài màng c?ng. T?p chí N?i khoa Vi?t Nam 16 (2013): 12-19.
- Davis RA. A long-term outcome analysis of 984 surgically treated herniated lumbar discs. J Neurosurg 80 (1994): 415-421.
- Chu TTL and Ph?m KL. ??c ?i?m lâm sàng và hình ?nh ch?p c?t l?p vi tính l?ng ng?c ? b?nh nhân giãn ph? qu?n t?i b?nh vi?n trung ??ng Thái Nguyên. Tr??ng ??i h?c Y D??c Thái Nguyên, B?n tin Y D??c h?c mi?n núi s? 4 n?m 2016, tr. 3-8.
- Riew KD, Park JB, Cho YS, Gilula L, Patel A, Lenke L, Bridwell K. Nerve root blocks in the treatment of lumbar radicular pain. A minimum five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88 (2006): 1722-1725.
- Runu R, Sinha NK, Pai R, Shankar PR, Vijayabhaskar P. Our experience with epidural steroid injections in management of low back pain and sciatica. Kathmandu Univ Med J 3 (2005): 349-354.


 Impact Factor: * 5.3
Impact Factor: * 5.3 Acceptance Rate: 73.64%
Acceptance Rate: 73.64%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 