Hydatid Cyst of the Liver: A Benign Disease that can be Life-Threatening
Mohamed Zouari*, Ahmed Khalil Ben Abdallah, Imen Abid, Riadh Mhiri
Department of pediatric surgery, Hedi-Chaker Hospital, Sfax, Tunisia
*Corresponding Author: Mohamed Zouari, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Hedi Chaker Hospital, 3029 Sfax, Tunisia
Received: 31 May 2019; Accepted: 14 June 2019; Published: 21 June 2019
Article Information
Citation: Mohamed Zouari, Ahmed Khalil Ben Abdallah, Imen Abid, Riadh Mhiri. Hydatid Cyst of the Liver: A Benign Disease that can be Life-Threatening. Journal of Surgery and Research 2 (2019): 32-33.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Liver, Cyst, Hepatic cysts, Surgery
Article Details
1. Case Report
One of the serious complications of liver hydatid cysts is cyst rupture. The surgical management of cyst rupture is difficult, and often associated with high morbidity and mortality rates [1, 2]. A 6-year-old boy who fell to the ground from a two meter high wall presented to the emergency department for complaints of dyspnea, cough, and abdominal pain. On examination, he had fever and tachypnea. In the computed tomography evaluation, the liver had multiple unilocular hepatic cysts in segments III, V, VII, and VIII. The hydatid cyst of the hepatic dome was complicated by pulmonary cracking with evidence of a fistulous pathway (Figure 1).
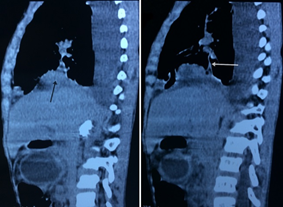
Figure 1: Coronary reconstruction of a thoracoabdominal tomodensitometry after injection of contrast medium showing a hydatid cyst of the hepatic dome (black arrow) complicated by pulmonary cracking with evidence of a fistulous pathway (white arrow).
There was also a right-sided pleural effusion. The patient underwent emergency surgery. After insertion of a chest tube into the fifth right intercostal space, a right subcostal lararotomy was performed. The ruptured hepatic cyst (Figure 2) was treated by cystectomy, excision of the germinative membrane, and closure of the fistulous tract with non-absorbable suture. Then the excision of the other hydatid cysts was performed. After operation, oral albendazole treatment (10 mg/kg) for 6 months was suggested as medical adjuvant treatment.
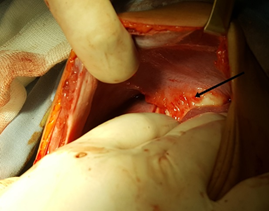
Figure 2: Intra-operative view after a laparotomy showing inflammatory adhesions between the hydatid cyst of the hepatic dome (arrow) and the diaphragm.
Conflict of Interest
None declared
Source of Support
Nil
References
- Rabiou S, Lakranbi M, Ouadnouni Y, et al. Surgical management of hydatid Bilio-bronchial fistula by exclusive thoracotomy. Int J Surg 41 (2017): 112-118.
- Toumi O, Noomen F, Salem R, et al. Intraperitoneal rupture of hydatid cysts. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 43 (2017): 387-391.


 Impact Factor: * 4.2
Impact Factor: * 4.2 Acceptance Rate: 72.62%
Acceptance Rate: 72.62%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 