Muco-hematic plugs as a cause of severe respiratory failure in COVID-19 patients
Sotirios M Malachias1, Effrosyni V Dima1, Konstantinos D Stamatis1, Eleni G Ischaki1*
Department of Intensive Care Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens Medical School, Evaggelismos General Hospital, Athens, Greece
*Corresponding author: Eleni G Ischaki, Department of Intensive Care Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens Medical School, Evaggelismos General Hospital, Athens, Greece
Received: 28 June 2021; Accepted: 05 July 2021; Published: 07 July 2021
Article Information
Citation: Sotirios M Malachias, Effrosyni V Dima, Konstantinos D Stamatis, Eleni G Ischaki. Muco-hematic plugs as a cause of severe respiratory failure in COVID-19 patients. Journal of Surgery and Research 4 (2021): 350-352.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
We present 2 cases of COVID-19 patients with almost complete airway obstruction by muco-hematic plugs. The plugs were finally removed and the microscopic examination revealed a mixture of mucin, blood, neutrophils, bronchial epithelial cells and bacteria
Keywords
<p>COVID-19, Muco-hematic plug, Airway obstruction</p>
Article Details
Case Presentation
The main bronchoscopic finding in COVID-19 ARDS is increased secretions, mostly copious and sometimes diffuse, white, jelly-like and difficult to suction [1]. We present the finding of haemorrhagic endobronchial casts in two COVID-19 patients. The first patient was intubated and mechanically ventilated with abrupt increase in peak pressure (>100cmH2O) and difficult ventilation [2]. The second patient was an extubated patient with intense cough and near complete laryngeal obstruction because of this cast. In the first patient bronchoscopy was performed and the initial image was a haemorrhagic, tissue-like saddle cast on carina, causing an almost complete occlusion of both main stem bronchus. This cast had the distal end tightly attached to the segmental and sub-segmental bronchi and could not be easily removed [3]. We managed to remove the vast majority of these casts using saline and a mucolytic agent (N-acetylcysteine) along with a biopsy forecep (Figure 1). Improvement of ventilation was noted immediately after the end of the procedure but the patient finally died because of uncontrolled endobronchial hemorrhage. In the second patient the cast was finally removed with the help of a respiratory physiotherapist. Microscopic examination of this tissue revealed a muco-hematic plug, infiltrated by neutrophils, bronchial epithelial cells and bacteria (Figure 2).
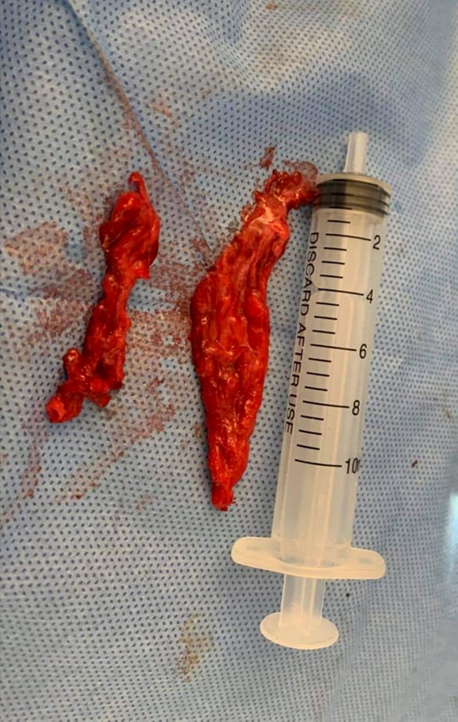
Figure 1: Bronchial muco-hematic plugs
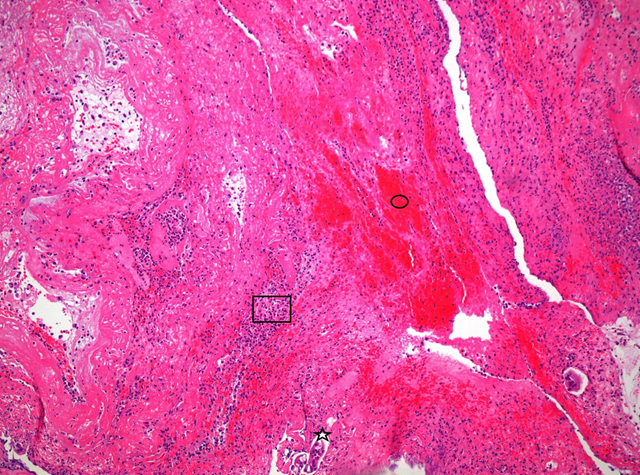
Figure 2: Microscopic examination of bronchial plugs:
? neutrophils, ? muco-hematic tissue, * bronchial epithelial cells
References
- Torrego A, Pajares V, Fernández-Arias C, et al. Bronchoscopy in Patients with COVID-19 with Invasive Mechanical Ventilation: A Single-Center Experience. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 202 (2020): 284-287.
- Wiles S, Mireles-Cabodevila E, Neuhofs S, et al. Endotracheal tube obstruction among patients mechanically ventilated for ards due to COVID-19: A Case Series. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine 36 (2021): 604-611.
- Herath S, Kruit N, Eslick A, et al. Haemorrhagic bronchial casts causing complete ventilatory failure in a COVID-19 patient on ECMO. Respirology Case Reports 8 (2020): e00631.


 Impact Factor: * 4.2
Impact Factor: * 4.2 Acceptance Rate: 72.62%
Acceptance Rate: 72.62%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 