Pneumocistis jiroveci Pneumonia in an AIDS-presenter Host: Missing the Target in the COVID-19 Epidemic
Vergori A1*, Mastrorosa I1, Pinnetti C1, Camici M1, Di Stefano F2, Mastrobattista A3, Vulcano A4, Bartolini B4, Granata G5, Topino S5, Amendola A6, Antinori A1
1HIV/AIDS Unit, National Institute for Infectious Diseases, Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS, Rome, Italy
2Radiology Unit, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS, Rome, Italy
3 Respiratory Infectious Diseases Unit, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS, Rome, Italy
4Microbiology Unit, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS, Rome, Italy
5Severe and Immunedepression-Associated Infectious Diseases Unit, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS, Rome, Italy
6Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases, Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS, Rome, Italy
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Alessandra Vergori, HIV/AIDS Unit, National Institute for Infectious Diseases L. Spallanzani, IRCCS, Via Portuense, 292-00149 Rome, Italy
Received: 07 August 2020; Accepted: 25 August 2020; Published: 21 September 2020
Article Information
Citation: Vergori A, Mastrorosa I, Pinnetti C, Camici M, Di Stefano F, Mastrobattista A, Vulcano A, Bartolini B, Granata G, Topino S, Amendola A, Antinori A. Pneumocistis jiroveci Pneumonia in an AIDS-presenter Host: Missing the Target in the COVID-19 Epidemic. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 4 (2020): 946-951.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
We report a case of a previously healthy man admitted with the suspicion of a COVID-19 pneumonia during the Italian pandemic. After 9 days the patient was diagnosed with a new HIV-1 infection with an etiologically confirmed Pneumocistis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP). With this description we would like to highlight the similarities of COVID-19 with PJP and that clinicians should consider other causative agents and that HIV testing should always be offered.
Keywords
<p>COVID-19, HIV; Pneumocistis jiroveci; interstitial pneumonia; AIDS-defining disease</p> <gdiv></gdiv>
Article Details
1. Introduction
Since 9 March, 2020 the World Health Organization has declared Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by SARS-CoV-2, a global pandemic with relevant health public and clinicians concerns [1] leading to potential misdiagnoses. For instance, it might be difficult to distinguish COVID-19 pneumonia from other viral and bacterial etiologies because of overlapping radiological and clinical features.
2. Case Report
We describe a case of a previously healthy man admitted to the emergency department after 5 days of fever, cough and dyspnea. On examination, he had tachypnea, tachycardia, normal blood pressure and the oxygen saturation was 96% while breathing ambient air at rest. On auscultation breath sounds were normal over the all lung areas, slightly decreased at the right basal segment. A chest high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan (images not available) revealed multiple ground glass opacities (GGOs), bilateral, partially consolidated with interlobular septa thickness and with a tendency to spare the basal segments of the lungs. Laboratory test results and arterial blood gases are shown in Table 1.
|
Laboratory Data |
||||
|
Variable |
Reference Range |
Emergency Department |
COVID-Hospital |
|
|
Day 1 |
Day 4* |
Day 39* |
||
|
Hemoglobin (g/dl) |
13.5-17.5 |
9.9 |
9.2 |
11.2 |
|
Hematocrit (%) |
41.0-53.0 |
30.7 |
29.1 |
35.5 |
|
White-cell count (per mm3) |
4500-11000 |
4.06 |
6070 |
5860 |
|
Differential count (%) |
||||
|
Neutrophils |
40-70 |
60.1 |
85.7 |
66.9 |
|
Lymphocytes |
22-44 |
33.7 |
8.2 |
21.5 |
|
Monocytes |
04-Nov |
5.2 |
6.1 |
10.9 |
|
Basophils |
0-3 |
0.2 |
0 |
0.7 |
|
Platelet count (per mm3) |
150000-400000 |
171000 |
192000 |
453000 |
|
C Reactive protein (mg/dl) |
<1 |
34.5 |
0.72 |
0.25 |
|
Activated partial-thromboplastin time (aPTT, sec) |
22.0-35.0 |
29.2 |
26 |
23.5 |
|
International normalized ratio |
0.80-1.20 |
1.14 |
1.07 |
0.93 |
|
D-dimer (ng/ml) |
<500 |
319 |
317 |
250 |
|
Sodium |
136-145 |
138 |
140 |
137 |
|
Potassium |
3.50-5.10 |
4.3 |
3.7 |
3.6 |
|
Creatinine (mg/dl) |
0.6-1.3 |
0.8 |
0.65 |
0.61 |
|
Urea nitrogen (mg/dl) |
20-50 |
20 |
24 |
27 |
|
Glucose (mg/dl) |
70-110 |
73 |
67 |
43 |
|
Ferritin (ng/ml) |
20-300 |
- |
1179 |
- |
|
Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) |
120-246 |
497 |
322 |
197 |
|
Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) |
May-40 |
51 |
26 |
14 |
|
Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) |
May-40 |
25 |
24 |
73 |
|
Fraction of inspired oxygen |
21% |
35% |
21% |
|
|
pH |
7.48 |
7.45 |
7.48 |
|
|
Partial pressure of oxygen (mmHg) |
67 |
141 |
100 |
|
|
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (mmHg) |
35 |
35 |
43 |
|
|
Oxygen saturation (%) |
96% |
100% |
99% |
|
|
PaO2/FiO2 (mmHg) |
319 |
402 |
595 |
|
*Day 4: admission at COVID hospital; day 39: weaning from oxygen therapy
Table 1: Laboratoristic and blood gases values.
The patient was referred to our institution after 3 days with the clinical and radiological suspicion of COVID-19 pneumonia. SARS-CoV-2 RNA was not detected by real-time PCR (RT-PCR) of two nasopharyngeal swabs. Investigations for other respiratory pathogens were also negative. Blood was tested for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), as per routine care, which came back reactive. Given the overall picture, a presumptive diagnosis of Pneumocistis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) was made and promptly, a specific therapy with cotrimoxazole double strength was initiated at therapeutic dosage (Trimetoprim 15 mg/kg/die IV divided q6h) plus tapering prednisone IV for 21 days. No allergic reactions were evident. The patient agreed for bronchoscopy; bronchial washings were taken from the lower lobes bilaterally: Pneumocistis jiroveci etiology was confirmed by RT-PCR, acid fast bacilli smear, PCR for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, bacterial culture and RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 were negative, and cytology ruled out malignancy. Moreover, ganciclovir was started as for disseminated CMV disease (sero-positivity of anti-CMV IgG, CMV DNA 270390 IU/mL, CMV antigen as 29 positive cells). Anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgG, Quantiferon test and Cryptococcus neoformans antigen resulted negative, HHV-8 DNA was undetectable. HIV-RNA was 1.454.246 copies/ml, CD4 count 19/mm3 (2,5 %), CD8 515/mm3 (65%) and CD4/CD8 ratio 0,04.
On day 6 after admission antiretroviral therapy with Bictegravir/Emtricitabine/Tenofovir alafenamide was initiated, it was well tolerated and the chest HRCT performed after 21 days of treatment showed a clear improvement (Figure 1a). On day 30 from the start of symptoms, the patient presented high fever with a progressive deterioration of respiratory function, requiring non-invasive mechanical ventilation. A chest HRCT scan revealed a worsening of GGOs which appeared much more diffuse (Figure 1b) compared with the previous HRCT exam (Figure 1a). The patient underwent a new bronchoscopy showing still the presence of Pneumocistis jiroveci by means RT-PCR, ruling out an unmasked TB and, again, SARS-CoV-2 infection. Serology testing for SARS-CoV-2 was negative. Viro-immunological reassessment showed HIV RNA 640 cps/ml with CD4 count 14/mm3 (4%). We considered the clinical and radiological worsening as a treatment failure and a second-line salvage treatment with Clindamycin IV and Primaquine per os was started plus high doses of prednisone. Rapidly, we observed an improvement of clinical conditions with resolution of fever and dyspnea and weaning from oxygen therapy.
PJP is a main issue in HIV immunocompromised hosts that exposes patients to high mortality rates, especially when the diagnosis is delayed. Since microbiological confirmation of PJP is difficult to obtain and not instantaneous, the diagnosis is often presumptive based on clinical, laboratoristic and radiological suspicion. PJP is a potential differential diagnosis for COVID-19 pneumonia, but in the context of this pandemic, it chances being missed, especially in case of unknown HIV infection. Peculiar radiological pattern of COVID-19 pneumonia have been already demonstrated [2-9] and radiologists must be aware that PJP at HRCT is a multifaceted process, with a variety of findings, along with a broad spectrum of infectious (e.g., viral, fungal, bacterial pneumonias) and non-infectious (e.g., pulmonary oedema, diffuse alveolar haemorrhage, and drug toxicity) differential diagnoses [10]. Nevertheless, the GGOs observed in the context of PJP might have a diffuse symmetric predominant distribution in the perihilar regions and the apices with peripheral sparing [11,13].
Although typical chest HRCT patterns of COVID-19 viral pneumonia include multifocal bilateral peripheral ground-glass areas associated with an interlobular septa thichkness (crazy paving pattern) subsegmental patchy consolidations, mostly subpleural, and predominantly involving lower lung lobes and posterior segments (Figure 1c) [2-9].
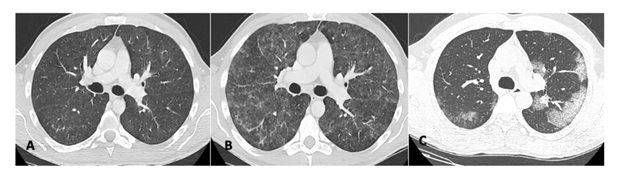
Figure 1A-1C: (1A) CT scan shows bilateral slight GGO areas with periferical sparing; (1B) Same patient as 1A with a severe progression of the interstitial impairment showing diffuse GGO; (1C) Image shows multiple ground-glass opacities with interlobular septal thickening showing a “crazy paving” pattern in the posterior segment of the upper left lobe and in the superior segments of both inferior lobes. The bilateralism of the peripheral lung opacities, without subpleural sparing, are common CT findings of the 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia.
In the case we describe, not only radiological features mimicked the SARS-CoV-2 etiology, but also hematological findings of both pathologies overlapped. Lymphopenia may be considered as a cardinal laboratory finding of SARS-CoV-2 infection and AIDS-related diseases, with a potential prognostic value, together with longitudinal evaluation of lymphocyte count dynamics and inflammatory indexes, including Lactate dehydrogenase, C Reactive Protein and ferritin [14].
With this case report, we would like to highlight the similarities of COVID-19 with PJP but we are not able to provide clues for the differential diagnosis. When treating a patient with suspected COVID-19 pneumonia, clinicians should consider other causative agents and HIV testing should be always offered.
Funding
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interests.
Author’s Statement
All the authors gave a substantial contribution to the manuscript.
References
- Bernheim A, Mei X, Huang M, et al. Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection. Radiology (2020): 200463.
- Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X, et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology 295 (2020): 202-207.
- Ye Z, Zhang Y, Wang Y, et al. Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review. Eur Radiol (2020): doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06801-0.
- Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, et al. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findings in 919 Patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 14 (2020): 1-7.
- Zhou S, Wang Y, Zhu T, et al. CT Features of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia in 62 Patients in Wuhan, China. AJR Am J Roentgenol 5 (2020): 1-8.
- Albarello F, Pianura E, Di Stefano F, et al. 2019-novel Coronavirus severe adult respiratory distress syndrome in two cases in Italy: An uncommon radiological presentation. Int J Infect Dis 93 (2020): 192-197.
- Zhao D, Yao F, Wang L, et al. A comparative study on the clinical features of COVID-19 pneumonia to other pneumonias. Clin Infect Dis (2020): pii: ciaa247.
- Pan Y, Guan H, Zhou S, et al. Initial CT findings and temporal changes in patients with the novel coronavirus pneumonia (2019-nCoV): a study of 63 patients in Wuhan, China. Eur Radiol (2020): 10.1007/s00330-020-06731-x.
- Cereser L, Dallorto A, Candoni A, et al. Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia at chest High-resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) in non-HIV immunocompromised patients: Spectrum of findings and mimickers. Eur J Radiol 116 (2019): 116-127.
- Bai HX, Hsieh B, Xiong Z, et al. Performance of radiologists in differentiating COVID-19 from viral pneumonia on chest CT. Radiology (2020).
- Kuhlman JE, Kavuru M, Fishman EK, Siegelman SS. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: spectrum of parenchymal CT findings. Radiology 175 (1990): 711-714.
- Zhao D, Yao F, Wang L, et al. A comparative study on the clinical features of COVID-19 pneumonia to other pneumonias. Clin Infect Dis (2020): pii: ciaa247.
- Terpos E, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Elalamy I, et al. Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19. Am J Hematol (2020): 10.1002/ajh.25829.


 Impact Factor: * 5.3
Impact Factor: * 5.3 Acceptance Rate: 75.63%
Acceptance Rate: 75.63%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 
