Syphilitic Leukoplakia
MJ Vivancos-Gallego1*, Mónica Garcia-Cosio2, Inmaculada Espinosa-Monroy1
1Department of Infectious Diseases. University Hospital Ramón y Cajal and IRYCIS, Universidad de Alcalá, Madrid, Spain; CIBERINFEC, Madrid, Spain
2Pathology, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, IRYCIS, Madrid, Spain; Universidad de Alcalá de Henares, Madrid, Spain; CIBERONC, Madrid, Spain
*Corresponding Author: M.J. Vivancos-Gallego, Department of Infectious Diseases. University Hospital Ramón y Cajal and IRYCIS, Universidad de Alcalá, Madrid, Spain; CIBERINFEC, Madrid, Spain.
Received: 20 October 2022; Accepted: 03 November 2022; Published: 31 January 2023
Article Information
Citation: MJ Vivancos-Gallego, Mónica Garcia- Cosio, Inmaculada Espinosa-Monroy. Syphilitic Leukoplakia. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 7 (2023): 42-43.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookKeywords
<p>Leukoplakia; Oral; Syphilis; Ulcer</p>
Article Details
1. Case Report
A 28-year-old male was referred by his primary care physician for work-up of possible oral candidiasis. He had been diagnosed with asymptomatic HIV-infection 18 months earlier and had undetectable viral load under antiretroviral treatment. The patient reported a history of multiple unprotected sexual encounters over the preceding 3 months. Physical examination showed painless and confluent whitish mucous patches (about 2 cm long) with erythematous border on the left soft palate which did not scrape off with a tongue depressor (Panel A). A biopsy specimen from the damaged mucosa was obtained and revealed hyperplasia of the epithelium and a dense inflammatory infiltrate in the corion, composed mainly by plasma cells (Panel B and C). Immunohistochemistry highlights numerous treponemal spirochetes, brown chromogen (Panel D and E). Treponemal tests (EIA and TPPA) were reactive and Rapid Plasma Reagin test (RPR) was positive (titer, 1:32). A diagnosis of syphilis was made. The patient was initially treated with intramuscular penicillin G benzathine. At 3-month follow-up he had complete resolution of palate lesion.
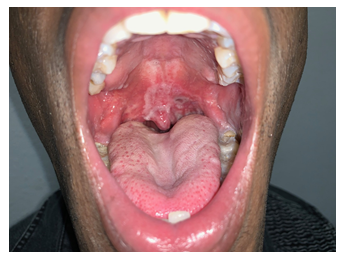
Panel A
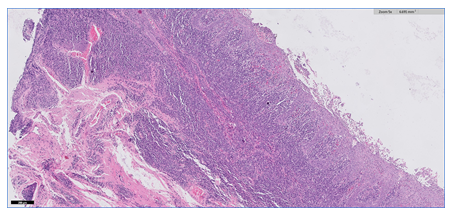
Panel B
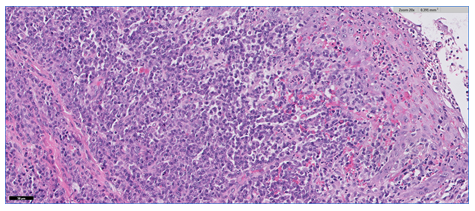
Panel C
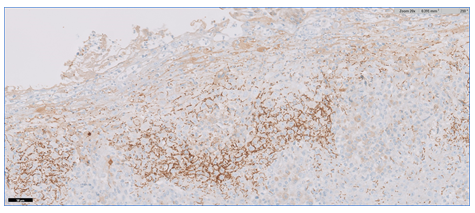
Panel D
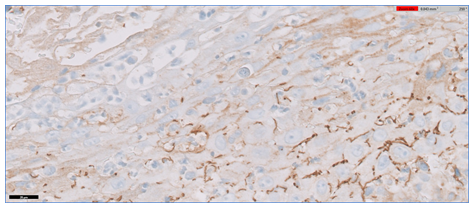
Panel E
Competing Interest
M.J.V.G reports grants and personal fees from Gilead and ViiV outside the submitted work. All other authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
M.J. V-G. is supported by a grant from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Contratos Juan Rodés, JR19/00031).


 Impact Factor: * 5.3
Impact Factor: * 5.3 Acceptance Rate: 75.63%
Acceptance Rate: 75.63%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 
